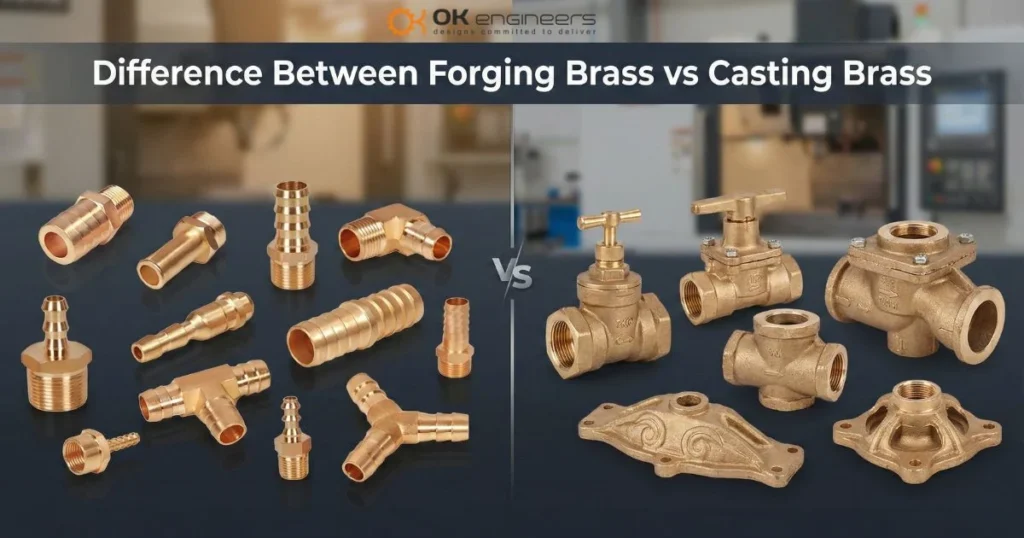
Choosing the right brass manufacturing method is not just a technical decision it directly affects strength, lifespan, safety, and cost. Many buyers, engineers, and procurement teams struggle to understand the Difference Between Forging Brass vs Casting Brass, which often leads to poor material selection and early component failure. At OK Engineers, we work closely with industries across plumbing, automotive, electrical, and architectural sectors. This guide explains Forging Brass vs Casting Brass in the clearest and most practical way possible so you can make the right decision the first time.
Understanding Brass as an Engineering Material
Brass is an alloy made primarily from copper and zinc, known for its:
- Corrosion resistance
- Excellent machinability
- Thermal and electrical conductivity
- Attractive gold-like appearance
Because of these properties, brass is widely used in:
- Plumbing fittings
- Valves and connectors
- Electrical components
- Decorative hardware
However, the Difference Between Forging Brass vs Casting Brass lies in how the metal is shaped, not what it’s made of—and that difference changes everything.
What Is Forging Brass?
Forging brass is a manufacturing process where heated brass billets are shaped using extreme compressive force through presses or hammers.
How Forging Brass Works
- Brass is heated below melting temperature
- High pressure forces it into dies
- Grain structure becomes compact and aligned
Key Benefits of Forging Brass
- Extremely high strength
- Dense internal structure
- Minimal air pockets (low porosity)
- Excellent pressure resistance
Forged brass components are widely trusted in critical load and pressure applications.
What Is Casting Brass?
Casting brass involves melting brass completely and pouring it into molds, where it cools and solidifies.
How Casting Brass Works
- Brass is melted at high temperature
- Liquid metal is poured into molds
- Component cools and is finished
Key Benefits of Casting Brass
- Complex and decorative shapes
- Lower tooling cost
- Ideal for artistic or low-stress parts
Casting offers more freedom—but at the cost of strength.
Difference Between Forging Brass vs Casting Brass
| Feature | Forging Brass | Casting Brass |
| Mechanical Strength | Very High | Moderate |
| Internal Structure | Dense & aligned | Random grains |
| Porosity | Almost none | Possible |
| Pressure Resistance | Excellent | Limited |
| Design Complexity | Moderate | High |
| Tooling Cost | Higher | Lower |
This table clearly shows the Difference Between Forging Brass vs Casting Brass in real-world terms.
Strength, Durability & Performance
Strength is where forging brass clearly dominates.
Forged Brass Performance
- Up to 30–40% stronger than cast brass
- Superior fatigue resistance
- Withstands vibration and thermal stress
Cast Brass Performance
- Suitable for static or decorative use
- Not ideal for high-pressure systems
- More prone to cracking under stress
This is why industries dealing with pipelines and sanitation similar to topics like Which Pipe Fitting is Used for Sanitary Pipes almost always choose forged brass.
Cost, Tooling & Production Efficiency
Forging Brass Cost Factors
- Higher initial tooling investment
- Faster cycle times for bulk production
- Very low rejection rates
Casting Brass Cost Factors
- Cheaper molds
- Higher finishing and inspection costs
- Greater material waste
| Cost Element | Forging Brass | Casting Brass |
| Initial Cost | High | Low |
| Long-Term Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Scrap Rate | Minimal | Moderate |
At OK Engineers, we recommend forging brass for high-volume and mission-critical parts.
Design Freedom & Shape Complexity
Casting brass allows complex internal cavities and artistic designs, making it popular for:
- Decorative hardware
- Sculptural components
- Lighting parts
This is why many Brass Lamp Parts Manufacturers rely on casting brass.
Forging brass, on the other hand, works best for:
- Symmetrical shapes
- Structural parts
- Functional components
Surface Finish, Accuracy & Machining
Forged brass offers:
- Smoother surfaces
- Better dimensional accuracy
- Easier CNC machining
Cast brass may require:
- Extra grinding
- Polishing
- Defect inspection
| Feature | Forged Brass | Cast Brass |
| Surface Quality | High | Moderate |
| Machining Time | Low | Higher |
| Accuracy | Excellent | Good |
Industrial Applications Explained
Best Uses for Forging Brass
- Plumbing valves and fittings
- Hydraulic components
- Automotive connectors
- Electrical terminals
Best Uses for Casting Brass
- Decorative fixtures
- Architectural hardware
- Low-load components
Knowing the Difference Between Forging Brass vs Casting Brass prevents costly failures and replacements.
Environmental & Sustainability Impact
Sustainability is a key ranking factor in modern manufacturing decisions.
Forging Brass
- Less material waste
- Lower energy use per part (in bulk)
- Longer product life
Casting Brass
- Higher energy consumption
- More scrap generation
- Still recyclable but less efficient
Forging supports eco-friendly manufacturing goals—something OK Engineers actively prioritizes.
How to Choose the Right Process
Choose Forging Brass if:
- Strength and pressure resistance matter
- Component failure is costly
- Production volume is high
Choose Casting Brass if:
- Design complexity is critical
- Load requirements are low
- Aesthetic value is priority
For maintenance and longevity similar logic used in guides like How to Clean Steel Fast & Easy forging brass usually wins.
Conclusion
The Difference Between Forging Brass vs Casting Brass ultimately comes down to performance versus flexibility. Forging brass delivers unmatched strength, durability, and reliability. Casting brass shines in design freedom and aesthetics. At OK Engineers, we help businesses select the right brass solution—ensuring safety, efficiency, and long-term value. Contact OK Engineers today to get expert guidance and premium-quality brass components.
FAQs
What is the main Difference Between Forging Brass vs Casting Brass?
Forging brass is stronger and denser, while casting brass allows complex shapes.
Is forged brass always better?
Not always. Forged brass is best for strength; cast brass is better for decorative designs.
Which brass is better for plumbing?
Forged brass is safer and longer-lasting.
Does OK Engineers manufacture both?
Yes, OK Engineers offers both forged and cast brass solutions.
Is cast brass recyclable?
Yes, but forging brass is more material-efficient.